티스토리 뷰
cluster를 여러 사람이 사용하기 위해서는 OS user를 각각 만들고, 각 OS user에게 특정 namespace만 Write할 수 있도록
허용해야 합니다.
이를 자동화하기 위한 Shell을 공유합니다.
k8s를 설치한 user 계정으로 수행해야 하며 그 유저는 sudo 권한이 있어야 합니다.
create-user 실행 파일 만들기
아래 내용으로 ~/.kube/create-user라는 shell파일을 만든 후 실행파일로 만드십시오.
$ cd ~/.kube
$ vi create-user
1) Ubuntu
#!/bin/bash
# Get parameter
if ([ $# == 0 ]) || ([ $# -eq 1 ] && [ "$1" == "-h" -o "$1" == "--help" ]); then
echo "create-user <user>"
echo " user: username"
echo "MUST RUN as root user or sudo's user."
exit 1
fi
OS=Unknown
hostnamectl | grep -q Ubuntu
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
OS=Ubuntu
fi
echo "OS: ${OS}"
if [ "${OS}" == "Unknown" ]; then
echo "Unsupported OS"
exit 1
fi
user=$1
grep -q ${user} /etc/passwd
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "${user} already exists"
else
sudo adduser --gecos "" ${user}
sudo usermod -aG docker ${user}
fi
# cp kubeconfig
sudo mkdir -p /home/${user}/.kube
sudo cp ~/.kube/config /home/${user}/.kube/
sudo cp ~/.kube/setup-config /home/${user}/.kube/
sudo chown -R ${user}:${user} /home/${user}/.kube
echo "${user} is created successfully!"
exit 0
2) CentOS
#!/bin/sh
# Get parameter
if ([ $# == 0 ]) || ([ $# -eq 1 ] && [ "$1" == "-h" -o "$1" == "--help" ]); then
echo "create-user <user>"
echo " user: username"
echo "MUST RUN as root user or sudo's user."
exit 1
fi
OS=Unknown
hostnamectl | grep CentOS 2>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
OS=CentOS
fi
hostnamectl | grep Ubuntu 2>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
OS=Ubuntu
fi
echo "OS: ${OS}"
if [ "${OS}" == "Unknown" ]; then
echo "Unsupported OS"
exit 1
fi
user=$1
grep ${user} /etc/passwd 2>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "${user} is already exists"
else
if [ "${OS}" == "CentOS" ]; then
sudo useradd ${user}
sudo passwd ${user}
else
sudo adduser ${user}
fi
sudo usermod -aG docker ${user}
fi
# cp kubeconfig
sudo mkdir -p /home/${user}/.kube
sudo cp ~/.kube/config /home/${user}/.kube/
sudo cp ~/.kube/setup-config /home/${user}/.kube/
sudo chown -R ${user}:${user} /home/${user}/.kube
echo "${user} is created successfully!"
exit 0$ chmod +x create-user
setup-config 실행 파일 만들기
아래 내용으로 ~/.kube/setup-config파일을 만들고, 실행파일로 변경하십시오.
$ cd ~/.kube
$ vi setup-config
1) Ubuntu
#!/bin/bash
echo "##### START of Setup kubeconfig! #####"
CLUSTER=`kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.clusters[].name}'`
NS=""
# Get parameter
if ([ $# == 0 ]) || ([ $# -eq 1 ] && [ "$1" == "-h" -o "$1" == "--help" ]); then
echo "setup-config [<CLUSTER>] <NAMESPACE>"
echo " CLUSTER: cluster명이며 기본값은 kubernetes이며 생략할 수 있음"
echo " NAMESPACE: namespace. 필수값임"
exit 2
fi
if [ $# == 1 ]; then
NS=$1
elif [ $# == 2 ]; then
CLUSTER=$1
NS=$2
fi
# check user and create if not
# Switch to kubernetes-admin context
#kubectl config use-context kubernetes-admin@kubernetes
# Create namespace if not exists
kubectl get ns | grep -q ${NS}
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create namespace ns-${NS} ]"
kubectl create ns ${NS}
else
echo "[ namespace ${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Create service account if not exists
kubectl get sa -n ${NS} | grep -q sa-${NS}
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create serviceaccount sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create sa sa-${NS} -n ${NS}
else
echo "[ serviceaccount sa-${NS} already exists in ${NS} ]"
fi
# Create secret for service accout: from k8s 1.24, secret for SA is not created automatically
cat <<EOF > secret.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: sa-${NS}
namespace: ${NS}
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: sa-${NS}
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
EOF
kubectl get secret -n ${NS} | grep -q sa-${NS}
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create secret sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml
else
echo "[ Already exists secret sa-${NS}. Delete it and recreate ]"
kubectl delete -f secret.yaml
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml
fi
# Create rolebinding: admin role for sa to created namespace
kubectl get rolebinding -n ${NS} | grep -q rb-sa-${NS}
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create rolebinding rb-sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create rolebinding rb-sa-${NS} --clusterrole=admin --serviceaccount=${NS}:sa-${NS} -n ${NS}
else
echo "[ rolebinding rb-sa-${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Create rolebinding: view clusterrole for sa to all namespace
kubectl get clusterrolebinding | grep -q crb-view-sa-${NS}
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create clusterrolebinding crb-view-sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create clusterrolebinding crb-view-sa-${NS} --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=${NS}:sa-${NS}
else
echo "[ clusterrolebinding crb-view-sa-${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Create Clusterrole 'crole-pv' which CRUD PV role.
cat <<EOF > crole-pv.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: crole-pv
rules:
- apiGroups: [ "", "storage.k8s.io" ]
resources: [ "persistentvolumes" ]
verbs: [ "create", "update", "patch", "delete", "get", "list", "watch" ]
EOF
kubectl get clusterrole crole-pv >/dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create clusterrole crole-pv ]"
kubectl apply -f crole-pv.yaml
else
echo "[ Already exists clusterrole crole-pv ]"
fi
# Create clusterrolebinding: PV CRUD clusterrole for sa to all namespace
kubectl get clusterrolebinding | grep -q crb-pv-sa-${NS}
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create clusterrolebinding crb-pv-sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create clusterrolebinding crb-pv-sa-${NS} --clusterrole=crole-pv --serviceaccount=${NS}:sa-${NS}
else
echo "[ clusterrolebinding crb-pv-sa-${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Get token of the serviceaccount
TOKEN=`kubectl describe secret sa-${NS} -n ${NS} | grep token: | cut -d ":" -f2 | tr -d " "`
# Create user
kubectl config view | grep -q "name: sa-{NS}"
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create user sa-${NS} in kubeconfig ]"
kubectl config set-credentials sa-${NS} --token=${TOKEN}
else
echo "[ User sa-${NS} already exists in kubeconfig ]"
fi
# Create context
kubectl config view | grep -q "name: ${NS}"
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create context ${NS} ]"
kubectl config set-context ${NS} --user=sa-${NS} --cluster=${CLUSTER} --namespace=${NS}
else
echo "[ Context ${NS} already exists in kubeconfig ]"
fi
# Test
current=`kubectl config current-context`
kubectl config use-context ${NS}
kubectl get all >/dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? == 0 ]; then
echo "SUCCESS to setup kubeconfig !!!"
else
echo "FAIL to setup kubeconfig !!!"
fi
# switch context or not
read -n 1 -p "context ${NS}로 전환하시겠습니까(y/n)? " yn
if [ "${yn}" == "y" ]; then
kubectl config use-context ${NS}
else
kubectl config use-context ${current}
fi
echo "##### END of Setup kubeconfig! #####"
exit 0
2) CentOS
#!/bin/sh
echo "##### START of Setup kubeconfig! #####"
CLUSTER=`kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.clusters[].name}'`
NS=""
# Get parameter
if ([ $# == 0 ]) || ([ $# -eq 1 ] && [ "$1" == "-h" -o "$1" == "--help" ]); then
echo "setup-config [<CLUSTER>] <NAMESPACE>"
echo " CLUSTER: cluster명이며 기본값은 kubernetes이며 생략할 수 있음"
echo " NAMESPACE: namespace. 필수값임"
exit 2
fi
if [ $# == 1 ]; then
NS=$1
elif [ $# == 2 ]; then
CLUSTER=$1
NS=$2
fi
# check user and create if not
# Switch to kubernetes-admin context
#kubectl config use-context kubernetes-admin@kubernetes
# Create namespace if not exists
chk=`kubectl get ns | grep ${NS}`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create namespace ns-${NS} ]"
kubectl create ns ${NS}
else
echo "[ namespace ${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Create service account if not exists
chk=`kubectl get sa -n ${NS} | grep sa-${NS}`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create serviceaccount sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create sa sa-${NS} -n ${NS}
else
echo "[ serviceaccount sa-${NS} already exists in ${NS} ]"
fi
# Create secret for service accout: from k8s 1.24, secret for SA is not created automatically
cat <<EOF > secret.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: sa-${NS}
namespace: ${NS}
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: sa-${NS}
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
EOF
secret=`kubectl get secret -n ${NS} | grep sa-${NS}`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create secret sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml
else
echo "[ Already exists secret sa-${NS}. Delete it and recreate ]"
k delete -f secret.yaml
k apply -f secret.yaml
fi
# Create rolebinding: admin role for sa to created namespace
chk=`kubectl get rolebinding -n ${NS} | grep rb-sa-${NS}`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create rolebinding rb-sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create rolebinding rb-sa-${NS} --clusterrole=admin --serviceaccount=${NS}:sa-${NS} -n ${NS}
else
echo "[ rolebinding rb-sa-${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Create rolebinding: view clusterrole for sa to all namespace
chk=`kubectl get clusterrolebinding | grep crb-view-sa-${NS}`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create clusterrolebinding crb-view-sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create clusterrolebinding crb-view-sa-${NS} --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=${NS}:sa-${NS}
else
echo "[ clusterrolebinding crb-view-sa-${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Create Clusterrole 'crole-pv' which CRUD PV role.
cat <<EOF > crole-pv.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: crole-pv
rules:
- apiGroups: [ "", "storage.k8s.io" ]
resources: [ "persistentvolumes" ]
verbs: [ "create", "update", "patch", "delete", "get", "list", "watch" ]
EOF
chk=`kubectl get clusterrole crole-pv`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create clusterrole crole-pv ]"
kubectl apply -f crole-pv.yaml
else
echo "[ Already exists clusterrole crole-pv ]"
fi
# Create clusterrolebinding: PV CRUD clusterrole for sa to all namespace
chk=`kubectl get clusterrolebinding | grep crb-pv-sa-${NS}`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create clusterrolebinding crb-pv-sa-${NS} ]"
kubectl create clusterrolebinding crb-pv-sa-${NS} --clusterrole=crole-pv --serviceaccount=${NS}:sa-${NS}
else
echo "[ clusterrolebinding crb-pv-sa-${NS} already exists ]"
fi
# Get token of the serviceaccount
TOKEN=`kubectl describe secret sa-${NS} -n ${NS} | grep token: | cut -d ":" -f2 | tr -d " "`
# Create user
chk=`kubectl config view | grep "name: sa-{NS}"`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create user sa-${NS} in kubeconfig ]"
kubectl config set-credentials sa-${NS} --token=${TOKEN}
else
echo "[ User sa-${NS} already exists in kubeconfig ]"
fi
# Create context
chk=`kubectl config view | grep "name: ${NS}"`
if [ $? == 1 ]; then
echo "[ Create context ${NS} ]"
kubectl config set-context ${NS} --user=sa-${NS} --cluster=${CLUSTER} --namespace=${NS}
else
echo "[ Context ${NS} already exists in kubeconfig ]"
fi
# Test
current=`kubectl config current-context`
kubectl config use-context ${NS}
kubectl get all
if [ $? == 0 ]; then
echo "SUCCESS to setup kubeconfig !!!"
else
echo "FAIL to setup kubeconfig !!!"
fi
# switch context or not
read -n 1 -p "context ${NS}로 전환하시겠습니까(y/n)? " yn
if [ "${yn}" == "y" ]; then
kubectl config use-context ${NS}
else
kubectl config use-context ${current}
fi
echo "##### END of Setup kubeconfig! #####"
exit 0$ chmod +x setup-config
OS 유저 계정 생성 및 kubernetes config 만들기
'user01'이라는 계정을 예로 설명하겠습니다.
1) OS user를 생성합니다.
# cd ~/.kube
# ./create-user user01
주의) minikube에서는 아래 작업을 먼저 하시고 진행 하십시오.
# chmod +r ~
# chmod +x ~
# chmod +r ~/.minikube/profiles/minikube/client.key
2) k8s config 생성
생성한 OS user로 바꾼 후 수행 합니다.
바꾼 user의 /home/{user명}/.kube디렉토리에는 위에서 만든 setup-config파일이 복사되어 있습니다.
현재 OS user를 위한 namespace를 만들고,
그 namespace에만 admin권한을 부여. 나머지 namespace에는 view권한만 부여.
* 마지막에 context전환을 물어보면 'y'를 눌러 새로 생성한 sevice account로 전환합니다.
# su - user01
$ cd .kube
$ ./setup-config {namespace}
ex) ./setup-config user01
3) admin 권한 회수
아래 명령으로 admin context와 admin user를 구합니다.
$ kubectl config view
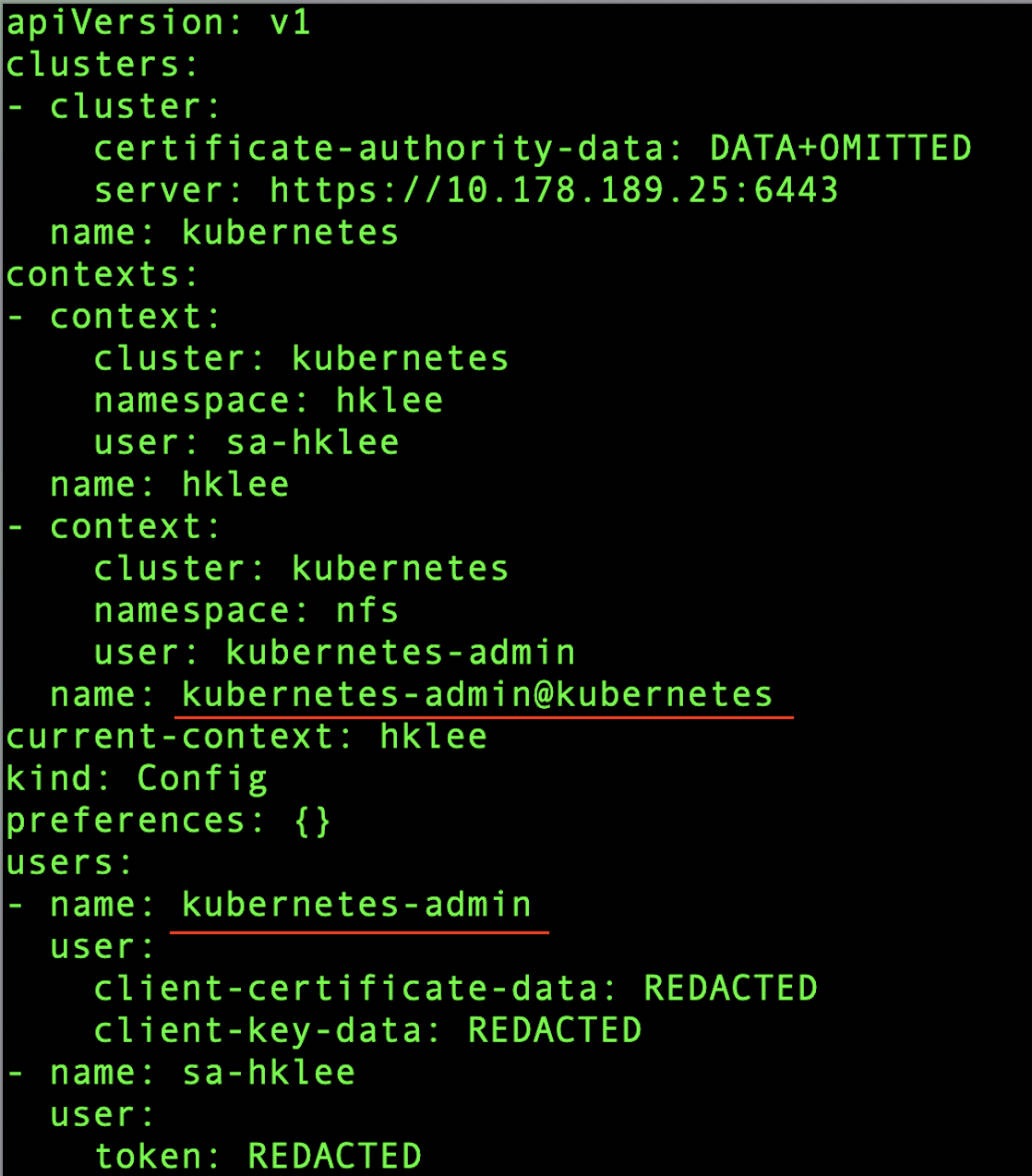
admin context를 삭제 합니다. 위 예제에서는 'kubernetes-admin@kubernetes'을 삭제합니다.
$ kubectl config delete-context kubernetes-admin@kubernetes
admin user를 삭제합니다. 위 예제에서는 'kubernetes-admin'을 삭제합니다.
$ kubectl config delete-user kubernetes-admin
'Cloud > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| kubernetes리소스 관리 유틸리티 k9s 소개 (1) | 2021.10.07 |
|---|---|
| kubernetes API Server의 IP 변경하기 (0) | 2021.08.23 |
| prometheus와 grafana를 이용한 통합모니터링 체계 구축 (2) | 2021.02.03 |
| EFK스택을 이용한 통합로깅체계 구축 (3) | 2021.02.02 |
| kubeconfig 셋팅 shell (0) | 2020.10.28 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 리퀴드폴리탄
- 호모프롬프트
- SAGA
- 버라이어티가격
- AI
- 마이크로서비스 패턴
- 디토소비
- 애자일
- 육각형인간
- agile
- 스포티파이
- 플러그인
- #MAS
- 분초사회
- 도파밍
- Event Sourcing
- 마이크로서비스
- API Composition
- agentic ai
- spotify
- 요즘남편 없던아빠
- 돌봄경제
- CQRS
- 스핀프로젝트
- micro service
- AXON
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
